PCB VS PCBA: Main Difference, Types, Cost & Quality Basic Standards
If there are two terms that are often used interchangeably in the electronics industry, they are PCB & PCBA. Yet are they the same? Definitely not! A Printed Circuit Board or PCB as it is popularly referred to is the underlying hardware that is used in electronic appliances. It can also be referred to as a blank or bare board. A PCBA on the hand, stands for Printed Circuit Board Assembly. While a PCB is a blank board, the assembly process ensures that all the components are mounted on it. It is after mounting all the components at the specified locations and integrating the circuits that a functional board is ready.
Let us look at both PCB & PCBA in some detail:
What Is PCB?
These blank boards are the basis of electronic devices and their use is therefore ubiquitous. Made up of fiberglass or composite epoxy they support the components that are placed on them. PCBs, in turn, are of several types:
Three Type of PCBs
1. Single-layer PCBs
These are the simplest type of PCBs that have a single layer of conducting material
2. Double-layer PCBs
These have a layer of conducting material on both the top and bottom of the board
YOU MAY ALSO LIKE: Single Sided Vs Double-Sided PCBs
3. Multi-layer PCBs
They have more than two conductive layers.
What does PCBA mean?
PCBA refers to complete PCB assembly that has all the electronic components in place to ensure effective functioning of the board. PCB Assembly largely uses two methods:
Types of PCBA
1. Surface-Mount Technology
SMT assembly involves mounting electronic components to the surface of the PCB. The steps involved here include:
- Preparing the PCB
- Placing the Components
- Reflow Soldering
- Inspection
2. Thru-Hole Technology
Through hole assembly is process that involves drilling holes in the PCB. It is through these holes that electronic components can be attached. This makes for strong connections between the board & the components & therefore to durable assemblies. The steps involved here include:
- Drilling the holes
- Placing the leads
- Soldering
- Inspection
While manufacturing a blank board is easier, as the above process shows, assembly is a fairly complex process that involves placing several components. With miniaturization of boards and increasing component density, the process is even more intricate.
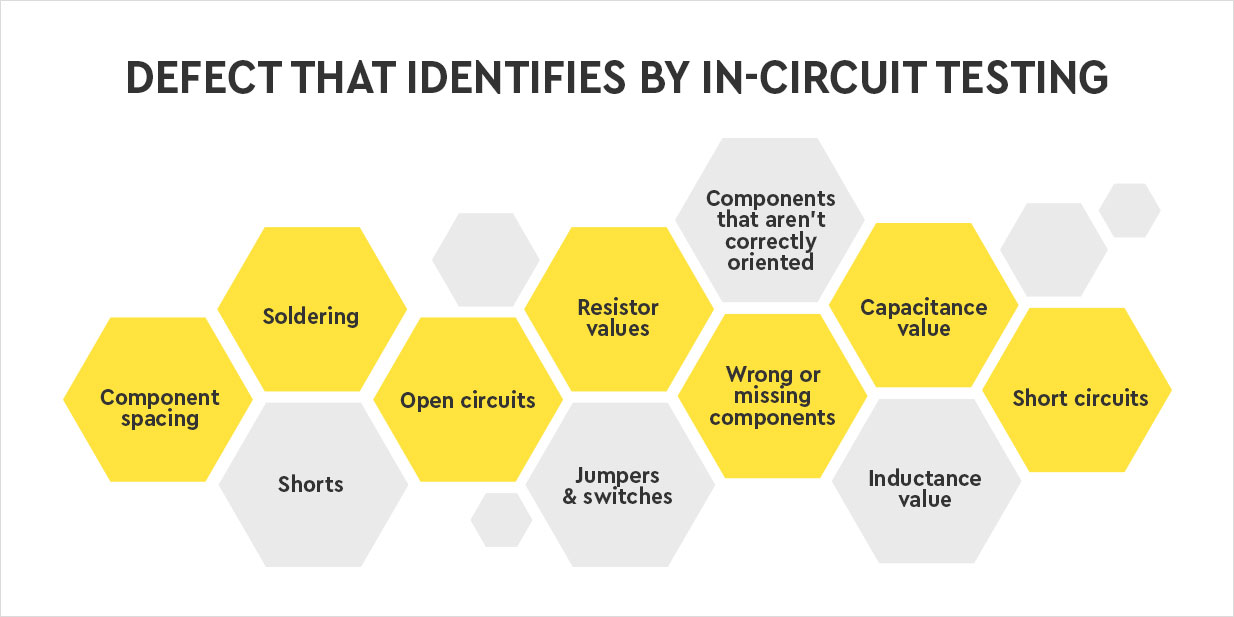
Also, while bare board testing is done by way of either Pinned Fixture Test or Flying Probe test. When it comes to testing of PCBA, there are a wide variety of tests including AOI, AOX, ICT, Smoke Testing, Black Box Testing, Regression Testing and more to ensure that the boards function effectively. Additionally, he boards need to adhere to specific IPC standards for PCB assembly.
Cost of PCBA
There are many factors that affect PCB assembly cost –
- Cost of Bare Board & Components
- Cost of labor
- Tooling cost
- Turnaround time involved
- Quantity required
- The technology being used
- Packaging specifications & more
Material Used in PCB and PCBA
Materials used in PCBs
There is a wide range of factors that lead to the choice of PCB material. Some of these include:
- Mechanical Strength
- Thermal Performance
- Dielectric Constant
- Temperature Resistance, and more
Types of materials used in PCB Manufacturing include:
1. FR-4
This is a commonly used material that comprises of a glass reinforced epoxy laminate sheet. It is particularly known for its tensile strength
2. Teflon
This is used in high-speed applications that require tight tolerances. That it is very light as well as flame resistant makes it extremely useful.
3. Metal
The use of metals such as copper, aluminum, iron is wide spread, these particularly work well where the PCBA process is done through SMT technology.
Materials used in PCBA
PCB Vs PCBA: Difference Between PCB Vs PCBA
Both PCB & PCBA are steps in the final production that goes into all electronic appliances. While a PCB is a blank circuit board, its assembly with various components leads to a functional board. While manufacturing a blank board is easier, assembly is a fairly complex process that involves placing several components. With miniaturization of boards and increasing component density, the process is even more intricate. In terms of cost also, while it is cheaper to produce a blank PCB, typically assembly of components costs more.
As a handy reckoner, the differences between PCB & PCBA can be summed up as below:
| Parameters | PCB | PCBA |
|---|---|---|
| Presence of Components | Bare Board with no components | Components are mounted |
| Turnaround Time | Is Quick | Assembly is an intricate process & takes time |
| Packaging used | Vacuum packing | Compartmental anti-static packing |
| Testing | Comparatively less | Complex & Stringent testing |